How to Set Up a GitHub Webhook in Jenkins
Integrating GitHub with Jenkins using webhooks is a powerful way to automate your CI/CD pipeline. Whenever you push code to your GitHub repository, a webhook can trigger a Jenkins job to build, test, or deploy your application. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to set up a GitHub webhook in Jenkins, complete with placeholders for images to help you visualize the process.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
A running Jenkins instance.
A GitHub repository.
Administrative access to both Jenkins and GitHub.
The GitHub plugin installed in Jenkins (usually installed by default).
Step 1: Configure Jenkins to Accept GitHub Webhooks
1.1 Set Up a Jenkins Job
Log in to your Jenkins dashboard.
Click on New Item to create a new job.
Enter a name for your job (e.g.,
GitHub-Webhook-Demo), select Freestyle project, and click OK.In the job configuration page:
Under Source Code Management, select Git.
Enter your GitHub repository URL (e.g.,
https://github.com/your-username/your-repo.git).Add credentials if your repository is private.
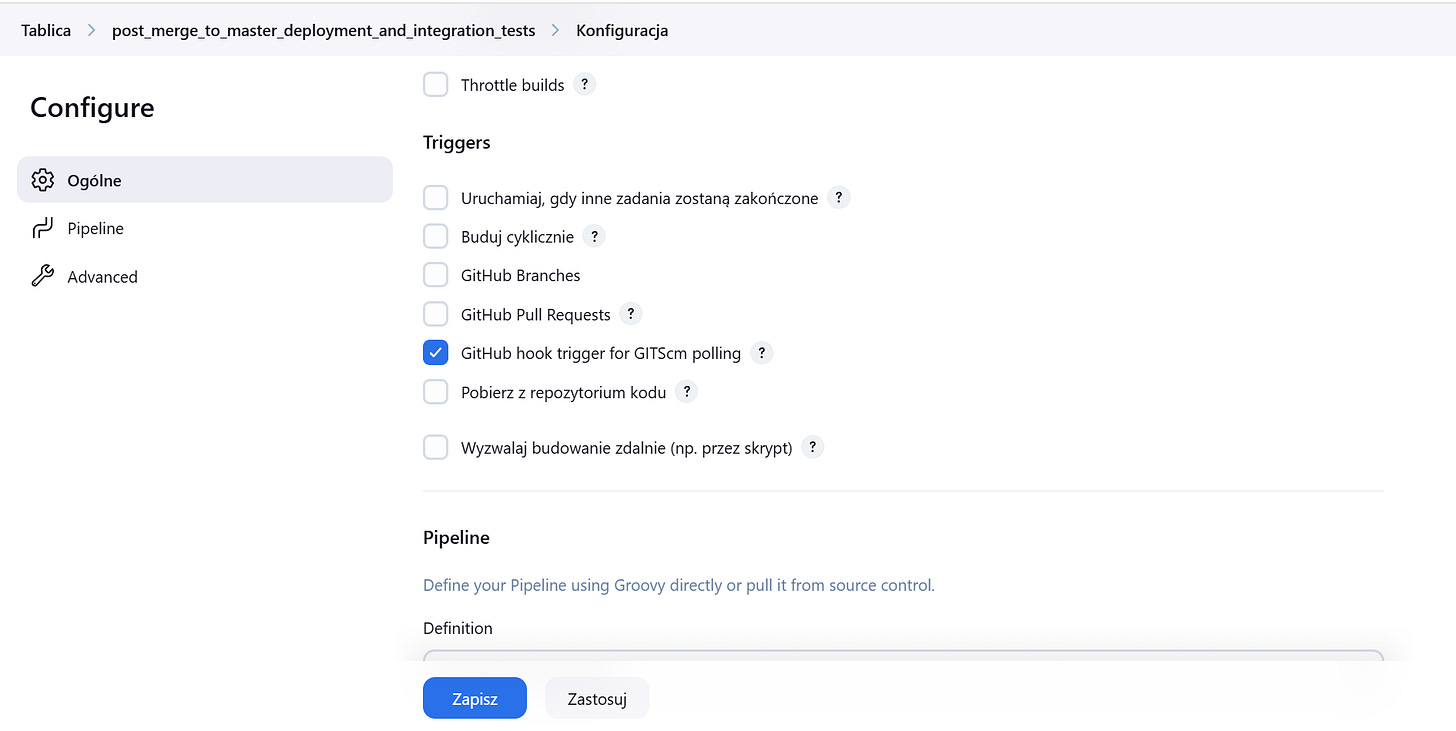
Under Build Triggers, check the box for GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling.
Save the job.
1.2 Configure Jenkins URL
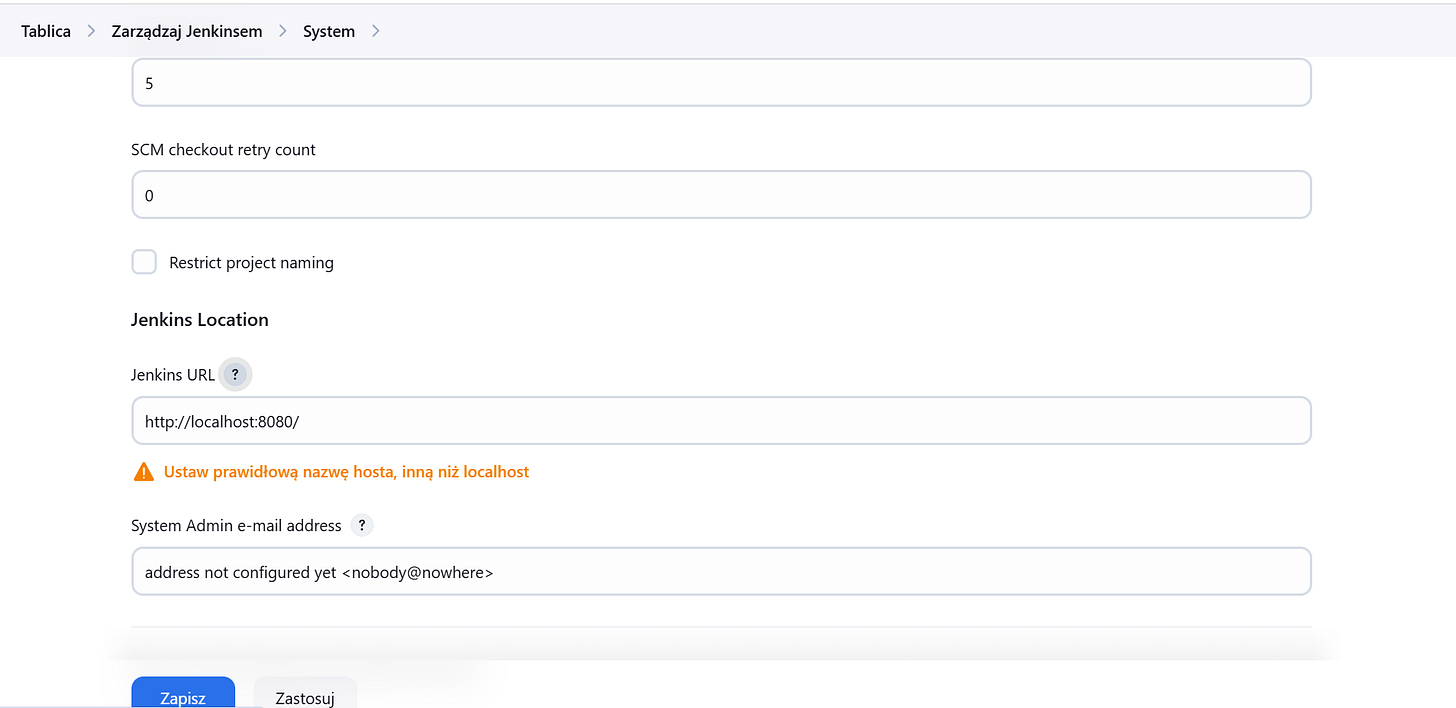
Go to Manage Jenkins > Configure System.
Ensure the Jenkins URL is correctly set (e.g.,
http://your-jenkins-server:8080
). This URL will be used by GitHub to send webhook payloads.
Save the configuration.
Step 2: Set Up the GitHub Webhook
2.1 Navigate to Your GitHub Repository
Go to your GitHub repository.
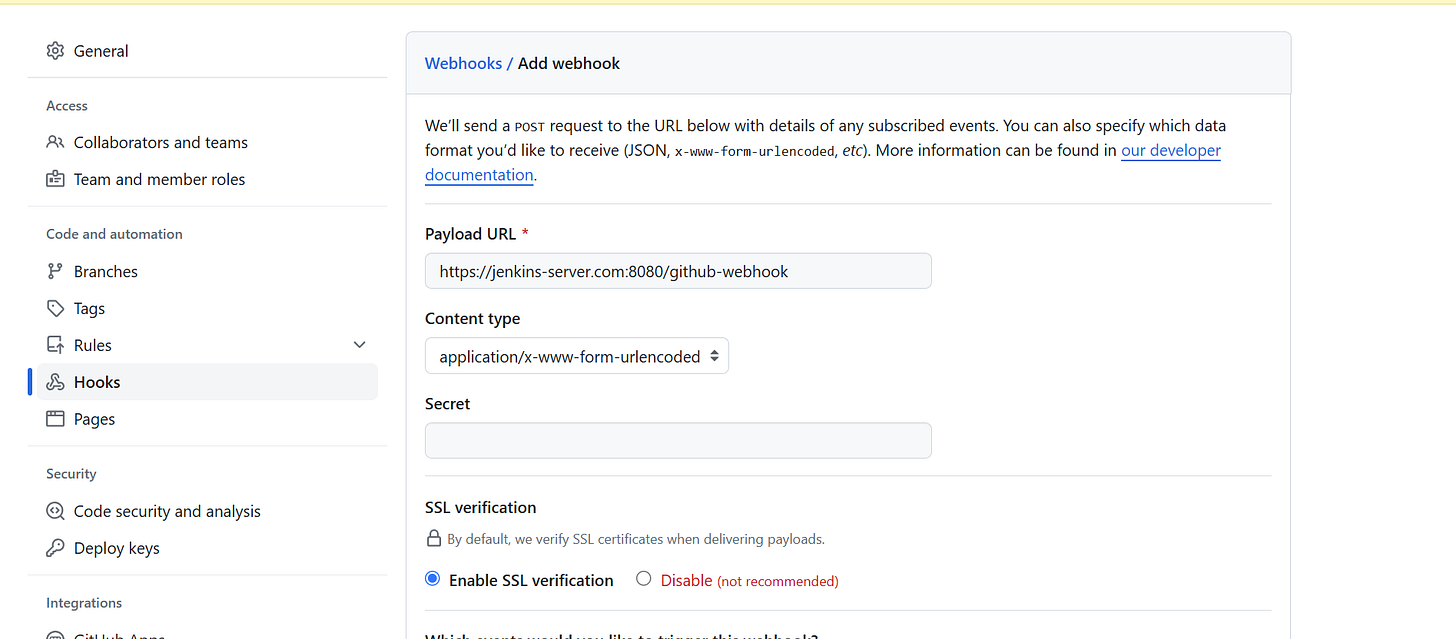
Click on Settings > Webhooks > Add webhook.
2.2 Configure the Webhook
In the Payload URL field, enter your Jenkins server URL followed by
/github-webhook/(e.g.,http://your-jenkins-server:8080/github-webhook/).Set the Content type to
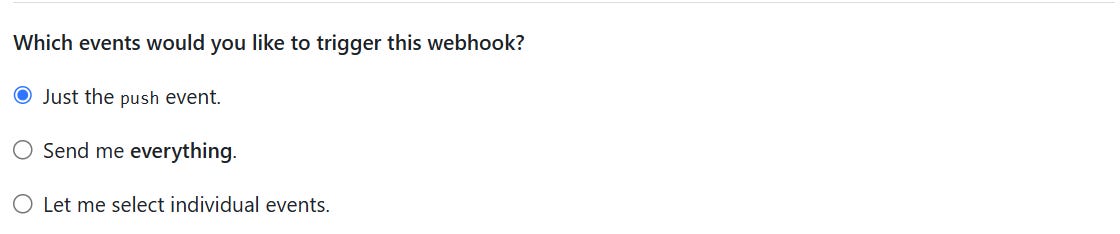
application/json.Under Which events would you like to trigger this webhook?, select Just the push event (or choose other events as needed).
Ensure the Active checkbox is checked.
Click Add webhook.
Step 3: Test the Integration
3.1 Make a Change in Your Repository
Make a small change to your repository (e.g., update a README file).
Push the changes to GitHub.
3.2 Verify the Webhook Trigger
Go to your Jenkins dashboard.
Check if the job you configured has been triggered automatically by the GitHub webhook.
Review the build logs to ensure everything is working as expected.
Step 4: Troubleshooting Tips
If the webhook doesn’t trigger the Jenkins job:
Check the GitHub webhook delivery logs for errors.
Ensure your Jenkins server is accessible from the internet (if using a public GitHub repository).
Verify that the Jenkins URL and webhook URL are correct.
Ensure the GitHub plugin is installed and up-to-date in Jenkins.
Conclusion
By setting up a GitHub webhook in Jenkins, you can automate your CI/CD pipeline and ensure that every code change triggers a build or deployment process. This integration saves time, reduces manual effort, and improves the efficiency of your development workflow.
Feel free to insert the relevant images in the placeholders provided to make this guide more visually engaging and easier to follow. If you encounter any issues, refer to the troubleshooting tips or consult the official documentation for Jenkins and GitHub.
Happy automating! 🚀